Signed in as:
filler@godaddy.com
Signed in as:
filler@godaddy.com
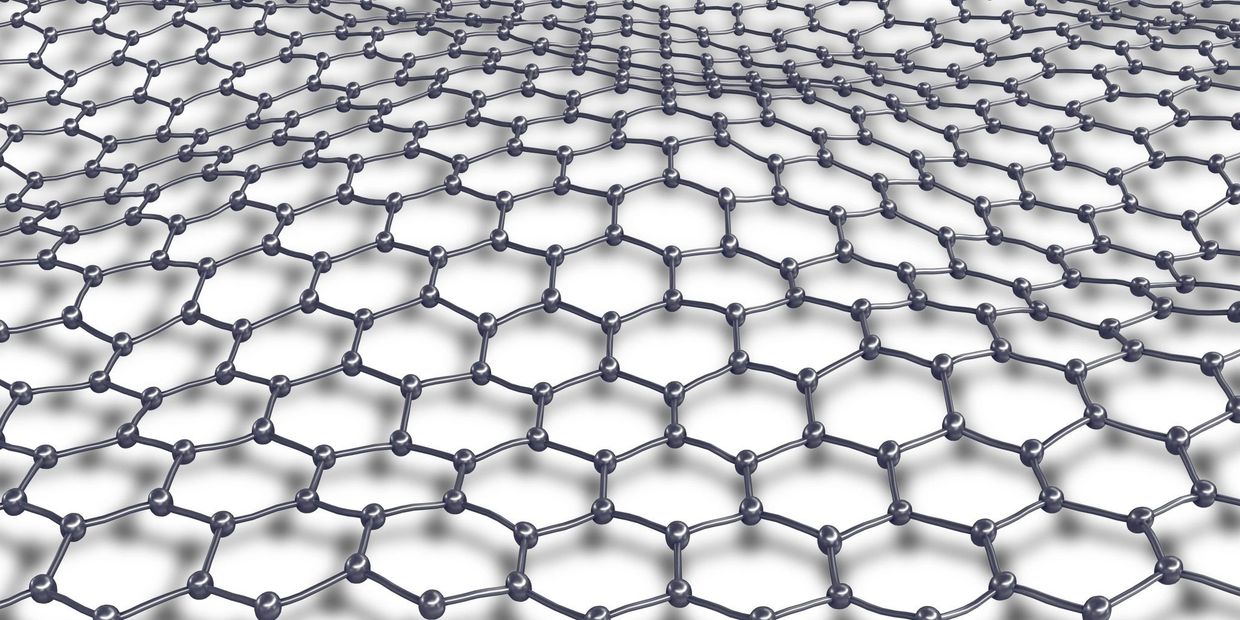
Take carbon atoms, arrange them in a hexagonal monolayer structure and you have pure graphene, which has been widely reported for its exceptional properties.
Graphene can be manufactured in a variety of methods, the details of which are protected trade secrets of their manufacturer but mainly centre around the exfoliation of graphite (a 3D structure comprising of 1000's of layers of graphene).
Most graphene produced today is in 'nanoplatelet' form, where there are usually no more than 10 layers stacked together. When you have 2 layers of graphene, it is called 'bi-layer' and somewhere in between these two is called 'few-layer'.
Graphene can impart an assortment of properties to host materials including enhancements of mechanical and thermal properties, as well as several secondary benefits such as antimicrobial, anti-static, ultraviolet (UV) and fire resistance with a bit of clever engineering.
A high carbon content (no unwanted atoms present in the structure) and low defections (where the carbon atoms are missing inter-connections).
It is extremely difficult for manufacturers to consistently make high quality graphene so picking the right supplier is essential.

High quality, single-layer graphene is transparent and nearly invisible to the human eye. That said, each layer of graphene absorbs around 3% of all light. Due to this, in its most common form as nanoplatelet powder, it is a black substance that in turn imparts a greyish colouration to whatever host material it is mixed with.

The carbon-carbon bond is one of the strongest in nature. Graphene’s many covalent bonds are strong and substantial energy is needed to break them. It also heralds great flexibility thanks to the flat arrangement of carbons.
Due to its large surface area, graphene interacts strongly with host polymers enhancing a whole range of mechanical properties.

Due to the arrangement of atoms, graphene has perfect thermal conduction properties and conducts in all directions. This conductivity is a result of free electrons that move unimpeded across the structure.
This conductivity can impart enhanced thermal transfer in host materials and can help speed up manufacturing processes.

Water based graphene dispersions are formulated to create Graphene-Wear™ formulations designed for textile coating (organics, synthetics and leathers).
The resultant graphene enhanced clothing print is the conduit that imparts the impressive properties explored across this website.

Graphene-Wear™ is available in a variety of high quality graphene enhanced raw materials right through to consumer product ready materials perfectly for improving the properties of sportswear, footwear and equipment.
We don't just operate as part of the supply chain, we partner with it. Not only this, but most of our customers are the brands that benefit from it.

Elastomers are enhanced using our graphene to create the impressive Graphene-Wear™ compounds, designed to be used for footwear, equipment and components.
The resultant materials boast the impressive properties also explored across this website.
Versarien Graphene Limited
Units 1A-D Longhope Business Park, Monmouth Road, Longhope, Gloucestershire, GL17 0QZ, United Kingdom